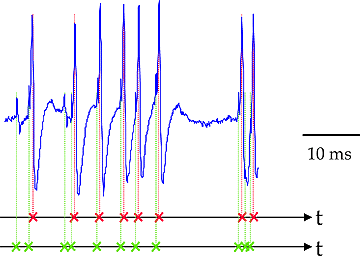
Information about sound is carried in the timing of the spikes. For example, loudness is usually coded by neurons in how rapidly the spikes occur.
Recorded spikes from a neuron in the auditory pathway

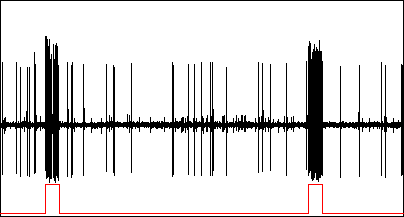
Response of an auditory neuron to a tone turned on every 6 seconds.

Back to the brain.
Don Johnson 3/16/97